Address: No. 92, Xidazhi Street, Nangang District, Harbin



JOIN-USHIT sincerely invite talents from both home and aproad to join in the new course of constructing first-class universities. |
Recently, Professor Yufei Ma’s team from the School of Astronautics at Harbin Institute of Technology has achieved high-sensitivity gas detection using light-induced thermoelastic spectroscopy (LITES) based on a perfect absorber coated quartz tuning fork (QTF). This research, titled Ultra-high Sensitive LITES Sensor Based on a Tri-layer Ultra-thin Perfect Absorber Coated T-head Quartz Tuning Fork, has been published in Laser & Photonics Reviews.
LITES demonstrates exceptional advantages, including excellent selectivity, high sensitivity, and rapid response speed, making it highly valuable for applications in environmental monitoring, fire warning, and medical diagnostics. As the core sensing element in the system, the QTF plays a pivotal role in determining detection performance. However, quartz has low absorbance for laser light in the wavelength range of 1-5μm, resulting in suboptimal photo-thermal-elastic-electric conversion efficiency and limiting further enhancement of LITES sensor capabilities.
To address this challenge, the research team developed a tri-layer ultra-thin perfect absorber on the electrode-free surface of a T-head QTF based on a streamlined theoretical framework based on admittance matching principles. This absorber demonstrates robust stability and reproducibility, significantly boosting the QTF’s absorption efficiency for 1530 nm light from less than 10% to 93%. This breakthrough enhances the photo-thermal-elastic-electric conversion efficiency and the detection sensitivity, achieving a 6.90-fold improvement in signal-to-noise ratio compared to the standard QTFs. Furthermore, the researchers integrated a 40 m fiber-coupled multi-pass cell and an erbium-doped fiber amplifier into the LITES sensing system. This configuration amplifies the laser-gas interaction and increases the laser power, enabling ultrahigh sensitive acetylene detection.
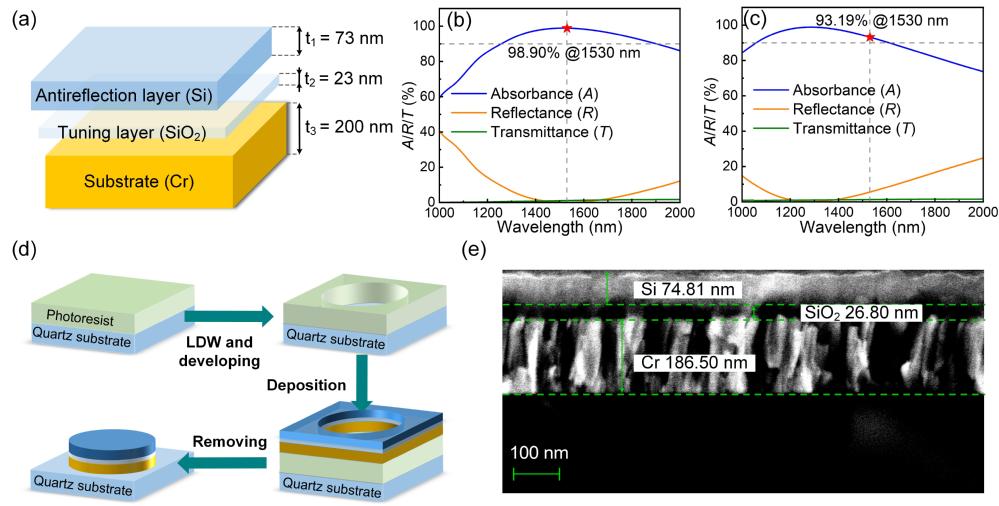
Figure 1. Theoretical and experimental results of the absorption membrane structure: a) schematic diagram of tri-layer structure; b) theoretical transmission, reflection, and absorption spectra; c) experimental transmission, reflection, and absorption spectra; d) sample preparation process; e) SEM cross-sectional image.
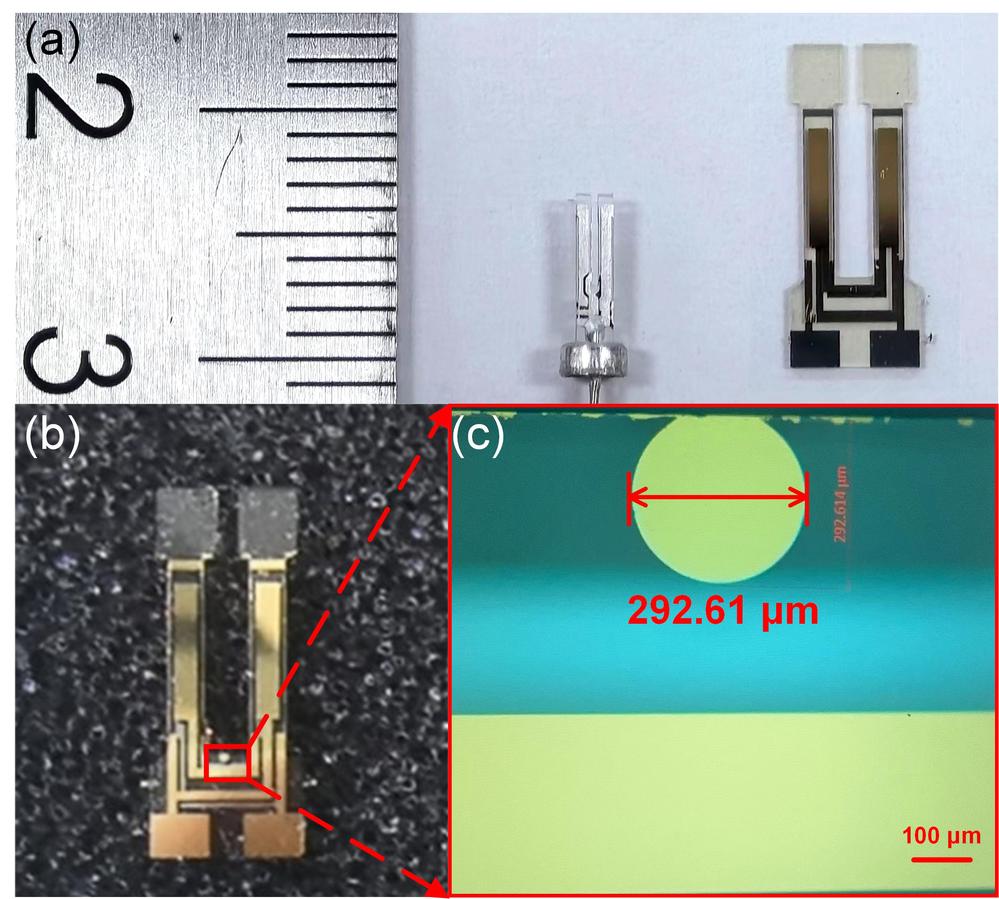
Figure 2. a) Photograph of a standard QTF (left) and a T-head QTF (right); b) photograph of a coated T-head QTF; c) microscopic image of the absorber.
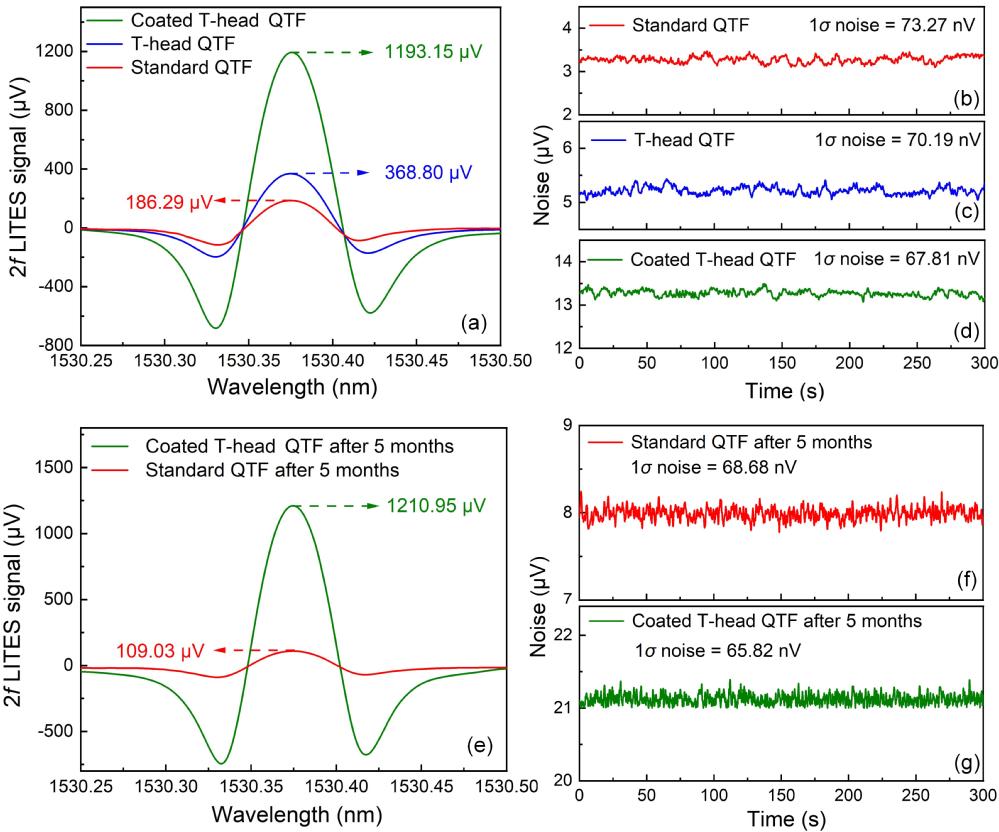
Figure 3. a) 2f signals recorded with the standard QTF, the T-head QTF and the tri-layer ultra-thin perfect absorber coated T-head QTF; the noise of b) the standard QTF, c) the T-head QTF and d) the tri-layer ultra-thin perfect absorber coated T-head QTF; e) 2f signals recorded with the standard QTF and the coated T-head QTF 5 months later; the noise of f) the standard QTF, and g) the coated T-head QTF 5 months later.
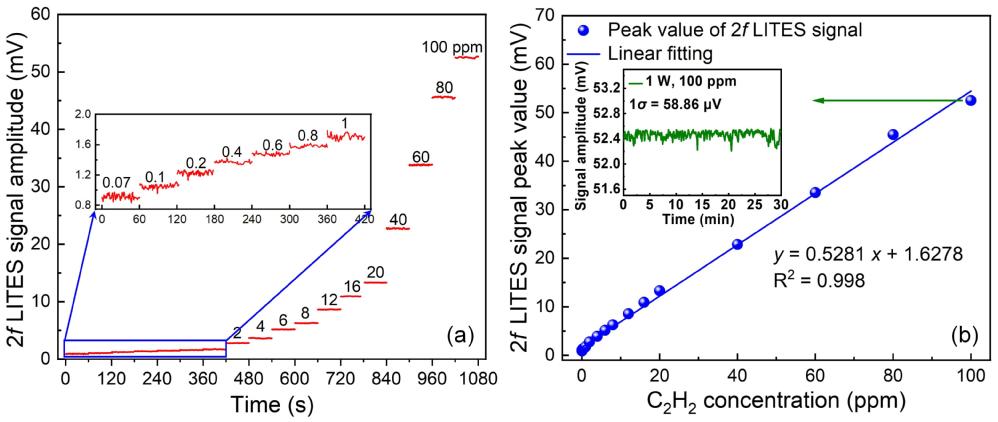
Figure 4. a) 2f signal amplitude measured under different C2H2 concentrations; b) 2f signal amplitude as a function of C2H2 concentrations, and the insert shows the 2f signal amplitude from continuous monitoring of 100 ppm C2H2 at 1 W laser power.
Harbin Institute of Technology is the first corresponding institution for the paper. Professor Yufei Ma from Harbin Institute of Technology and Professor Shaowei Wang from the Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, serve as the co-corresponding authors of the paper. Runqiu Wang, a doctoral student from the School of Astronautics, is the first author of the paper. Doctoral students Xueyu Guan and Qixiang Jia from the Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, as well as Associate Professor Ying He and Associate Researcher Shunda Qiao from the School of Astronautics, participated in the relevant research work or provided guidance for the paper.
This research was funded by the Key Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Young Scientists Studio of Harbin Institute of Technology, et al.
Paper link: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/lpor.202402107